Twitterbots: Anatomy of a Propaganda Campaign
Internet Research Agency archive reveals a vast, coordinated campaign that was incredibly successful at pushing out and amplifying its messages.
Key Findings
- The operation was carefully planned, with accounts often registered months before they were used – and well in advance of the 2016 U.S. presidential election. The average time between account creation and first tweet was 177 days.
- A core group of main accounts was used to push out new content. These were often ”fake news” outlets masquerading as regional news outlets or pretended to be political organizations.
- A much larger pool of auxiliary accounts was used to amplify messages pushed out by the main accounts. These usually pretended to be individuals.
- The campaign directed propaganda at both sides of the liberal/conservative political divide in the U.S., in particular the more disaffected elements of both camps.
- Most accounts were primarily automated, but they would frequently show signs of manual intervention, such as posting original content or slightly changing the wording of reposted contented, presumably in an attempt to make them appear more authentic and reduce the risk of their deletion. Fake news accounts were set up to monitor blog activity and automatically push new blog posts to Twitter. Auxiliary accounts were configured to retweet content pushed out by the main accounts.
- The most retweeted account garnered over 6 million retweets. Only a small fraction (1,850) of those retweets came from other accounts within the dataset, meaning many of the retweets could have come from genuine Twitter users.
One of the main talking points of the 2016 U.S. presidential election campaign involved attempts to surreptitiously influence public opinion using social media campaigns. In the months after the election, it quickly became apparent that a sophisticated propaganda operation had been directed against American voters.
Not surprisingly, news of these campaigns caused widespread public concern, prompting social media firms to launch investigations into whether their services had been misused. In October 2018, Twitter released a massive dataset of content posted on its service by the Internet Research Agency (IRA), a Russian company responsible for the largest propaganda campaign directed against the U.S.
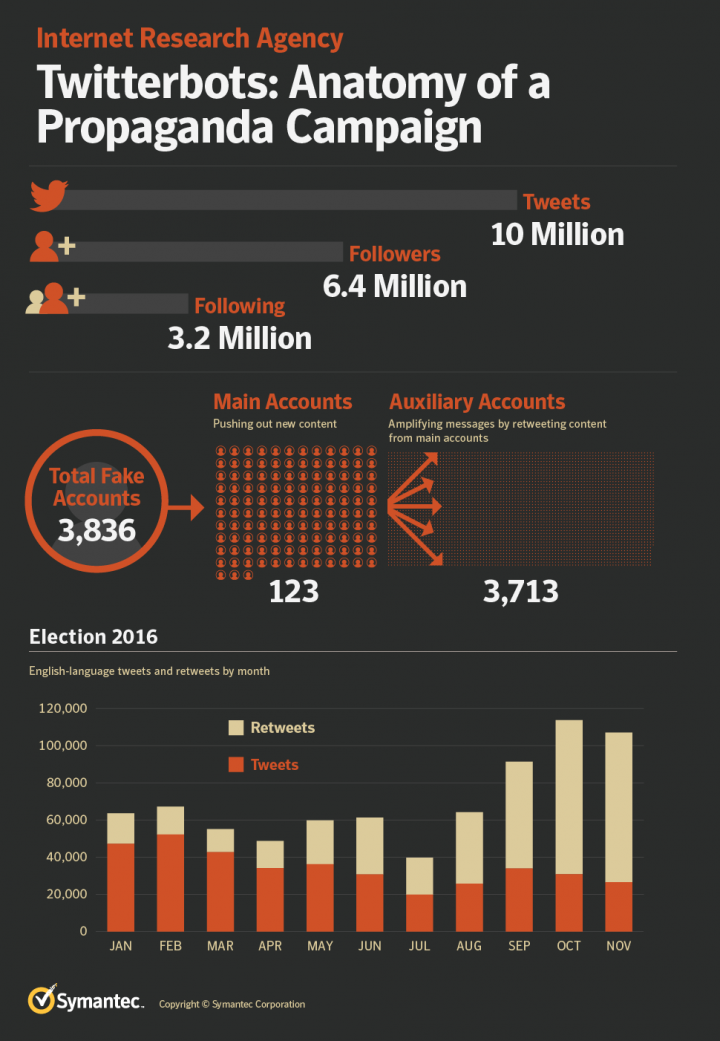
The dataset consisted of 3,836 Twitter accounts and nearly 10 million tweets. These accounts had amassed almost 6.4 million followers and were following 3.2 million accounts. The sheer volume of data was enormous, more than 275 GB.
The archive has proven to be a treasure trove of information on how the IRA’s propaganda campaign operated. For example, prior to the release, many people assumed that its posts were focused on just one side of the political spectrum. Once the data was made public, it quickly became obvious that in order to achieve its goal, the campaign directed propaganda at both sides of the liberal/conservative political divide in the U.S., in particular the more disaffected elements of both camps. The main objective of the campaign instead appeared to be sowing discord by attempting to inflame opinions on both sides. This was not just confined to the online sphere. Several of the accounts were used to organize political rallies in the U.S. and some of the most influential accounts in the dataset were used to promote these events to the largest possible audience.
However, believing that there is a lot to learn from this data beyond its messages and target audience, we decided to carry out some in-depth analysis of the archive to learn more about how this propaganda campaign worked. What we discovered was that this was not an ad-hoc response to political events in the U.S. Instead, the evidence points to a carefully planned and coordinated operation, with the groundwork often laid months in advance.
While the tactics employed changed somewhat over time, the basic template for this operation remained the same, utilizing a small core of accounts to push out new content and a wider pool of automated accounts to amplify those messages.
Along the way, we also came across some interesting bits of information, such as what appeared to be some rogue operators using monetized link-shortening services to make some money on the side.
Different account types
Once we started analyzing the data, it became apparent that the accounts could be divided into two main categories, which we called main accounts and auxiliary accounts. Each category had different characteristics and played a different role.
Main accounts had at least 10,000 followers but followed substantially fewer accounts. They were primarily used to publish new tweets.
Auxiliary accounts had less than 10,000 followers, but often followed more accounts than that. Their main purpose was to retweet messages from other accounts, although they were also used to publish original tweets. Not surprisingly, the majority of accounts were auxiliary accounts. We identified 123 main accounts and 3,713 auxiliary accounts within the dataset.
Main accounts generally were ”fake news” outlets masquerading as regional news outlets, or pretending to be political parties or hashtag games—the popular Twitter game that involves people sharing anecdotes or jokes based on a single theme, such as #5WordsToRuinADate. Based on their creation date they were usually created individually or in small batches. The default language selected for main accounts was always either English or Russian.
Auxiliary accounts usually pretended to be individuals, spreading the content created by the main accounts by retweeting it. These accounts were usually created in batches and sometimes hundreds of auxiliary accounts were created on the same day. For example, during May 2014, seven fake news accounts were set up by the agency, along with 514 auxiliary accounts.
Many of the accounts were created long before they were used. The average time between account creation and first tweet was 177 days. The average length of time an account remained active was 429 days.
Influential accounts
Some of the Twitter accounts created by the attackers managed to be extraordinarily influential. The most retweeted account within the dataset was TEN_GOP. Created in November 2015, the account masqueraded as a group of Republicans in Tennessee. It appears to have been manually operated.
In less than two years TEN_GOP managed to rack up nearly 150,000 followers. Despite only tweeting 10,794 times, the account garnered over 6 million retweets. Only a tiny fraction (1,850) of those retweets came from other accounts within the dataset. In other words, almost all of its retweets came from accounts outside the dataset, meaning many could have been real Twitter users.
Due to the popularity of this account, the IRA created two backup accounts in case TEN_GOP should be discovered and shutdown—ELEVEN_GOP and realTEN_GOP—both of which have the same profile description: “This is our backup account in case anything happens to @TEN_GOP”.
As has already been noted, the IRA’s campaign targeted both ends of the political spectrum in the U.S. and this is reflected in the breakdown of influential accounts. The top 20 most retweeted English-language accounts were split evenly between conservative and liberal messages.
| User name | Profile description | Retweets | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEN_GOP | Unofficial Twitter of Tennessee Republicans. Covering breaking news, national politics, foreign policy and more. #MAGA #2A | 6,000,296 | |
| Crystal1Johnson | It is our responsibility to promote the positive things that happen in our communities. | 3,776,481 | |
| Pamela_Moore13 | Southern. Conservative. Pro God. Anti Racism | 2,223,854 | |
| wokeluisa | APSA. #Blackexcellence. Political science major | 1,217,081 | |
| JemiSHaaaZzz | Teacher, Reader, Writer, Resister. #Resistance RESPECT LOVE LOYALTY | 1,171,652 | |
| KaniJJackson | Follow the example set by Mrs Obama; peace, love, acceptance & vigilance #Impeach45 #Resist #GunReformNow | 821,178 | |
| gloed_up | No black person is ugly #BRONZE #BlackLivesMatter #BlackToLive | 787,521 | |
| TrayneshaCole | Love for all my people of Melanin. Your BLACK is BEAUTIFUL! #MyPussyMyChoice #BlackGirlsMagic #BlackLivesMatter | 585,768 | |
| Jenn_Abrams | Calm down, I'm not pro-Trump. I am pro-common sense. Any offers/ideas/questions? DM or email me [email protected] (Yes, there are 3 Ns) | 559,978 | |
| SouthLoneStar | Proud TEXAN and AMERICAN patriot #2a #prolife #Trump2016 #TrumpPence16 Fuck Islam and PC. Don't mess with Texas! | 557,781 | |
| BlackNewsOutlet | Freedom is never given; it is won. #BlackLivesMatter | 491,973 | |
| BlackToLive | We want equality and justice! And we need you to help us. Join our team and write your own articles! DM us or send an email: [email protected] | 478,238 | |
| TheFoundingSon | Business Owner, Proud Father, Conservative, Christian, Patriot, Gun rights, Politically Incorrect. Love my country and my family #2A #GOP #tcot #WakeUpAmerica | 454,868 | |
| BleepThePolice | For a second at least, I'm resurrecting the peace #Blacktivist #BlackLivesMatter | 306,157 | |
| USA_Gunslinger | Truth is strong, and sometime or other will prevail! | 267,192 | |
| tpartynews | [NO DATA] | 144,508 | |
| PamelaKealer13 | [NO DATA] | 114,198 | |
| Jeblary2016 | 2016 US presidential candidate | 106,553 | |
| 10_gop | Conservative, daily news that you won't find on mainstream media. #MAGA Retweeted by @realDonaldTrump 😇 | 105,587 | |
| Blk_Voice | Activist. Feminist. Celebrating and highlighting Black excellence. | 103,967 |
There is a similar split in themes in the breakdown of the most followed English language accounts. Thirty-five percent pretended to support conservative causes, while 30 percent pretended to back liberal causes. The remainder masqueraded as general or political news outlets.
| User name | Profile description | Number of followers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEN_GOP | Unofficial Twitter of Tennessee Republicans. Covering breaking news, national politics, foreign policy and more. #MAGA #2A | 147,767 | |
| Jenn_Abrams | Calm down, I'm not pro-Trump. I am pro-common sense. Any offers/ideas/questions? DM or email me [email protected] (Yes, there are 3 Ns) | 79,152 | |
| Pamela_Moore13 | Southern. Conservative. Pro God. Anti Racism | 72,121 | |
| TodayNYCity | New York City's local news on Twitter. Breaking news, sports, events and international news. Tweet us or DM | 66,980 | |
| ELEVEN_GOP | This is our back-up account in case anything happens to @TEN_GOP | 59,279 | |
| wokeluisa | APSA. #Blackexcellence. Political science major | 57,295 | |
| Crystal1Johnson | It is our responsibility to promote the positive things that happen in our communities. | 56,581 | |
| SouthLoneStar | Proud TEXAN and AMERICAN patriot #2a #prolife #Trump2016 #TrumpPence16 Fuck Islam and PC. Don't mess with Texas! | 53,999 | |
| TheFoundingSon | Business Owner, Proud Father, Conservative, Christian, Patriot, Gun rights, Politically Incorrect. Love my country and my family #2A #GOP #tcot #WakeUpAmerica | 47,413 | |
| USA_Gunslinger | Truth is strong, and sometime or other will prevail! | 44,895 | |
| WashingtOnline | Breaking news, weather, traffic and more for Washington. DM us anytime. RTs not endorsements | 40,762 | |
| BlackNewsOutlet | Freedom is never given; it is won. #BlackLivesMatter | 40,458 | |
| Politweecs | Tweets and politics | 36,094 | |
| NewOrleansON | Breaking news, weather, traffic and more for New Orleans and Louisiana. DM us anytime. RTs not endorsements | 35,988 | |
| KaniJJackson | Follow the example set by Mrs Obama; peace, love, acceptance & vigilance #Impeach45 #Resist #GunReformNow | 34,276 | |
| WarfareWW | Political & Military Analyst | 33,375 | |
| PigeonToday | America’s Weakest Primetime Lineup Anywhere! Follow Merica's #1 cable news network, delivering you breaking news, insightful analysis, and must-see memes. | 32,347 | |
| BlackToLive | We want equality and justice! And we need you to help us. Join our team and write your own articles! DM us or send an email: [email protected] | 29,472 | |
| KansasDailyNews | Local news, sports, business, politics, entertainment, travel and opinion for Kansas. DM us 24/7 | 29,357 | |
| gloed_up | No black person is ugly #BRONZE #BlackLivesMatter #BlackToLive | 28,943 |
Fake news
Most of the fake news accounts created by the agency pretended to be local news outlets, such as “New Orleans Online”, “El Paso Top News”, or “San Jose Daily”. The majority of these accounts were created between May and August of 2014, but lay dormant until January 2015, when most of them started tweeting. This suggests that the fake news element of the operation was planned well in advance.
The vast majority (96 percent) of these fake news accounts were fully automated, using services to monitor blog activity and automatically push new blog posts to Twitter. Another two percent of these accounts queued tweets for publication at scheduled times.
Most followed a broad pattern of activity, with activity trending upwards from the beginning of 2015 until the summer of 2016 when there was a sudden fall in activity. By August 2016, all but one fake news account had stopped tweeting.
This is likely because the fake news accounts had been using a service known as Twitterfeed to feed their blogs to Twitter. During 2016, Twitterfeed announced that it would close by October of that year and the fake news accounts began to transition to an alternative service called Twibble. The drop off in activity during August 2016 could have been caused by technical problems during the changeover. By December the changeover was complete and the fake news accounts had resumed business as usual.
Prolific accounts
Not surprisingly, a majority (55 percent) of the most prolific accounts were fake news accounts. However, a significant number of prolific accounts had their identities masked by Twitter because they had less than 5,000 followers. Most of these accounts acted as auxiliary accounts and were automated in the same manner as most of the fake news accounts. However, while fake news accounts were automated to publish original content, these other accounts were automated to retweet content.
| User name | Display name | User profile description | English language tweet count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymized | Anonymized | No more #HappyHolidays shit!!! It's #MerryChristmas!!!!! #BuildTheWall #DrainTheSwamp #MAGAus¸ @realDonaldTrump | 133,315 | |
| TodayNYCity | New York City Today | New York City's local news on Twitter. Breaking news, sports, events and international news. Tweet us or DM | 58,630 | |
| ChicagoDailyNew | Chicago Daily News | Local news, sports, business, politics, entertainment, travel and opinion for Chicago and Illinois. DM us 24/7 | 53,071 | |
| KansasDailyNews | KansasCityDailyNews | Local news, sports, business, politics, entertainment, travel and opinion for Kansas. DM us 24/7 | 51,648 | |
| ScreamyMonkey | Screamy Monkey | First frontier.News aggreagtor. | 45,947 | |
| NewOrleansON | New Orleans Online | Breaking news, weather, traffic and more for New Orleans and Louisiana. DM us anytime. RTs not endorsements | 45,894 | |
| DailySanFran | San Francisco Daily | Follow for San Francisco's breaking news, special reports, entertainment and more from @DailySanFran | 44,711 | |
| Anonymized | Anonymized | Never Eat These Foods | 44,416 | |
| Anonymized | Anonymized | All major information policy in the world, we are ready to give you the most accurate and timely information in the field of politics and economics | 35,016 | |
| Anonymized | Anonymized | Wife, Mother, Patriot, Friend | 34,251 | |
| TodayPittsburgh | Pittsburgh Today | Pittsburgh's local news on Twitter. Breaking news, sports, events and international news. Tweet us or DM | 33,104 | |
| WashingtOnline | Washington Online | Breaking news, weather, traffic and more for Washington. DM us anytime. RTs not endorsements | 32,880 | |
| RoomOfRumor | Room Of Rumor | [NO DATA] | 31,126 | |
| Seattle_Post | Seattle Post | Be the first to know Seattle's local news. Politics, sport, entertainment, business, features and more that you need to know and share | 29,821 | |
| OnlineCleveland | Cleveland Online | Breaking news, weather, traffic and more for Cleveland. DM us anytime. RTs not endorsements | 27,291 | |
| WorldOfHashtags | World Of Hashtags | Hosted by @GiselleEvns. Join #WorldOfHashtags game on Mondays at 9AM ET/ Wednesdays at 10AM ET | 26,417 | |
| PhoenixDailyNew | Phoenix Daily News | Local news, sports, business, politics, entertainment, travel and opinion for Phoenix and Arizona. DM us 24/7 | 25,730 | |
| Anonymized | Anonymized | Workout Advice for a better life. | 25,453 | |
| gloed_up | 1-800-WOKE-AF | No black person is ugly #BRONZE #BlackLivesMatter #BlackToLive | 25,366 | |
| DetroitDailyNew | Detroit Daily News | Local news, sports, business, politics, entertainment, travel and opinion for Detroit. DM us 24/7 | 25,193 |
Following the links
Some tweets within the dataset contained links to other content. The majority of links were shortened URLs, masking the final destination. To get a picture of which sites these tweets were linking to, we followed each shortened URL tweeted during 2016 to find out the ultimate link destination. The largest number of links led to other Twitter posts, some of which were to other suspended accounts.
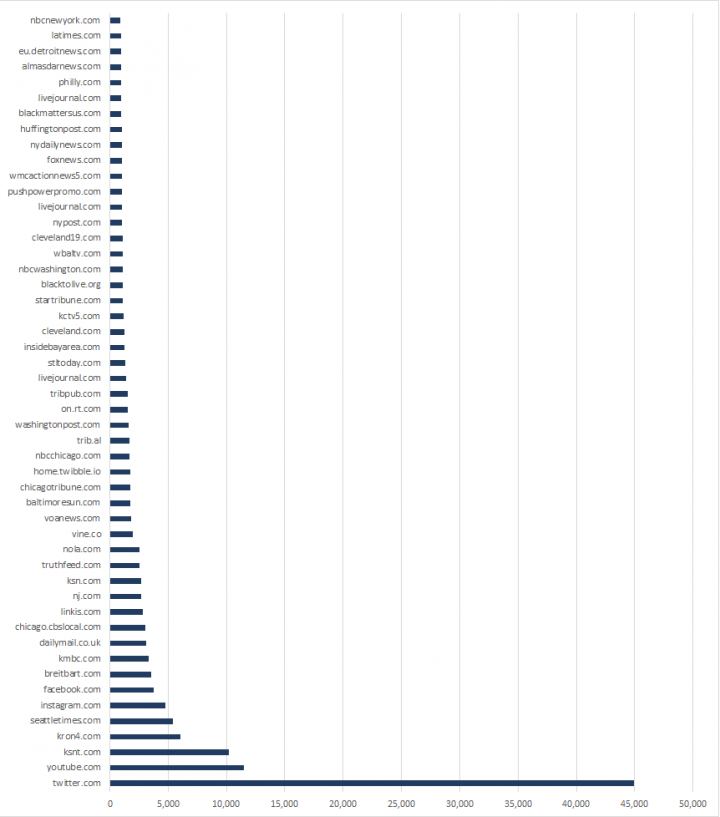
Aside from Twitter, other social media services such as YouTube, Instagram, and Facebook also figured highly in the list of websites being linked to. The rest of the list was mostly filled out by links to legitimate media outlets. This suggests that, along with delivering “fake news” the campaign also leveraged real news stories that supported messages it was pushing.
2016 U.S. presidential election
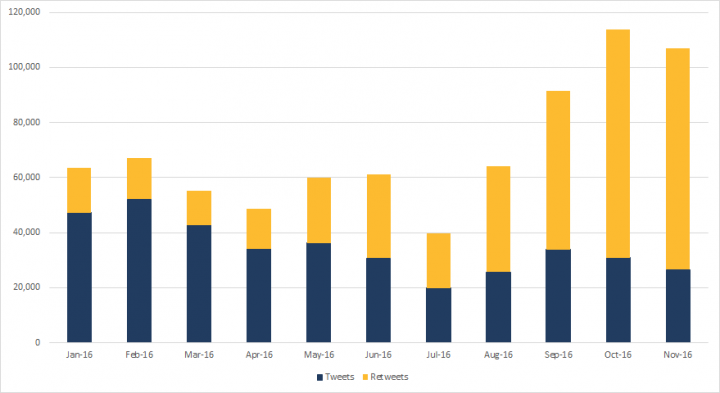
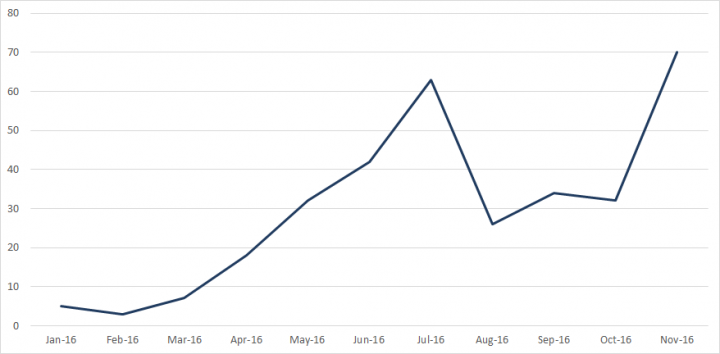
During the months prior to the 2016 U.S. presidential election, there was a marked increase in activity. Between January and November 2016, accounts within the dataset sent 771,954 English language tweets, with a marked uptick in activity as November approached.
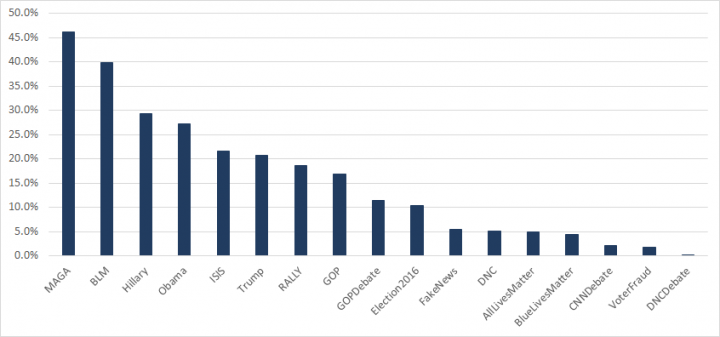
Analysis of the topics tweeted by English language accounts during this time period reveals that content was heavily focused on the election and quite evenly split between topics relating to either side of the political spectrum in the U.S.
Political rallies
Perhaps the most overt aspect of the propaganda campaign was the IRA’s organization of a number of political rallies in the U.S. Despite the fact that the accounts comprised of fake personas and organizations, they nevertheless succeeded in mobilizing people to attend events. Besides its online activities, the campaign’s operators also organized rallies supporting positions on both sides of the political spectrum.
One account, @March_for_Trump, advertised more events than any other account in the dataset, promoting events 47 times. Most of the other accounts involved in promoting rallies are anonymized as they have less than 5,000 followers.
Only nine accounts in the dataset retweeted March_for_Trump’s tweets promoting rallies, but the majority of these retweets came from the most followed or retweeted accounts in the dataset, suggesting the campaign’s operators had prioritized promoting these events.
Professional campaign
While this propaganda campaign has often been referred to as the work of trolls, the release of the dataset makes it obvious that it was far more than that. It was planned months in advance and the operators had the resources to create and manage a vast disinformation network.
It was a highly professional campaign. Aside from the sheer volume of tweets generated over a period of years, its orchestrators developed a streamlined operation that automated the publication of new content and leveraged a network of auxiliary accounts to amplify its impact.
The sheer scale and impact of this propaganda campaign is obviously of deep concern to voters in all countries, who may fear a repeat of what happened in the lead-up to the U.S. presidential election in 2016.
A growing awareness of the disinformation campaigns may help blunt their impact in future. If you’re concerned about falling victim to similar campaigns, read our blog post How to Spot a Twitter Bot, which can be found on Symantec’s Election Security blog.






We encourage you to share your thoughts on your favorite social platform.