
In the security field, virtual machines (VM) have been used for many years and are popular among researchers because malware can be executed and analyzed on them without having to reinstall production systems every time. As we previously discussed, these tests can be done manually or on automated systems, with each method providing different benefits or drawbacks. Every artifact is recorded and a conclusion is made to block or allow the application. For similar reasons, sandbox technology and virtualization technology have become a common component in many network security solutions. The aim is to find previously unknown malware by executing the samples and analyzing their behavior.
However, there is an even bigger realm of virtual systems out there. Many customers have moved to virtual machines in their production environment and a lot of servers are running VM, performing their daily duty with real customer data.
This leads to a common question when talking to customers: “Does malware detect that it is running on a virtual system and quit?”
Some customers still hope that the answer is yes and that they are immune to malware when running virtual systems. Unfortunately, this is a misconception.
It is true that some malware writers try to detect if their creation is running on a VM. Some of the tricks used to detect if a program is running in a virtual environment are quite simple:
- Check the MAC address of the virtual network adapter to reveal the vendor
- Check certain registry keys that are unique to virtual systems
- Check if helper tools like VMware tools are installed
- Check for certain process and service names
- Check for communication ports and behavior
- Execute special assembler code and compare the results
- Check the location of system structures, like the descriptor tables
Malware has one huge advantage when executed on an automated VM analysis system. The analysis system needs to make a decision in a reasonable timeframe and if the sample does not behave in a malicious manner within the first five minutes, such as skipping waiting loops, the system will most likely deem it harmless. Other tricks used to detect a virtual machine focus on the malware interaction. For example, malware can wait for the system to reboot twice before it starts acting malicious or it can activate the payload after a certain number of mouse clicks have occurred. These tricks are harder to patch within automated VMs.
In some rare cases we have encountered malware that does not quit when executed on a virtual machine, but instead sends false data. These “red herrings” might ping command-and-control servers that never existed or check for random registry keys. These tactics are meant to confuse the researcher or have the automation process declare the malware a benign application.
Most of the samples use a runtime packer with built in VM detection. Generally, this means the packer or crypter will perform the detections, not the sample itself. Malware authors have realized that it is suspicious when an application detects that it is running on a VM, so they have stopped using those features in recent years.
Malware authors want to compromise as many systems as possible, so if malware does not run on a VM, it limits the number of computers it could compromise. So, it should not come as a surprise that most samples today will run normally on a virtual machine and that the features can be added if the cybercriminal wishes to do so.
Figure 1. Packer tool VM detection options
In order to answer the initial question with some real data and not just a gut feeling, we selected 200,000 customer submissions since 2012 and ran them each on a real system and on a VMware system and then compared the results. I tried my best to filter out samples that crashed before leaving traces or those that left “red herring” traces. For the last two years, the percentage of malware that detects VMware hovered around 18 percent with a short spike at the beginning of 2014 where it reached 28 percent. On average, one in five malware samples will detect virtual machines and abort execution.
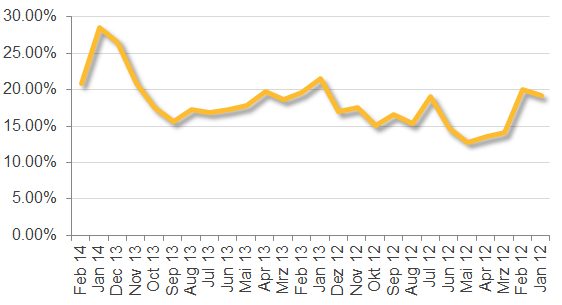
Figure 2. Malware samples that detect VMware per month
This means that malware still detects if it is running on a VM, but only in some minor cases. Symantec recommends that virtualized systems, just like any other systems, should be properly protected in order to keep them safe from threats.
Symantec engineers are always on the lookout for new techniques that malware authors may employ to bypass automated analysis. With the combination of various proactive detection methods, like reputation based detection, we can ensure maximum security for our customers.
For more information on threats to virtual machines, read our whitepaper: Threats to Virtual Environments